Abstract
Background
We reported durable responses to CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell therapy (JCAR014) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients (pts) after prior failure of ibrutinib (Turtle, JCO 2017; NCT01865617). In those pts, ibrutinib was not administered during CAR-T cell immunotherapy. Continuation of ibrutinib through leukapheresis, lymphodepletion and CAR-T cell therapy may prevent tumor progression after ibrutinib withdrawal, mobilize tumor into the blood, improve CAR-T cell function, and decrease cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
Methods
We conducted a phase 1/2 study of CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy in R/R CLL pts and established a regimen of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine (Cy/Flu) lymphodepletion followed by JCAR014 at 2 x 106 CAR-T cells/kg (Turtle, JCO 2017). We then compared outcomes of these pts (No-ibr cohort) with a subsequent cohort that received Cy/Flu with 2 x 106/kg JCAR014 CAR-T cells with concurrent ibrutinib (420 mg/d) from at least 2 weeks prior to leukapheresis until at least 3 months after JCAR014 infusion (Ibr cohort). Dose reduction was permitted for toxicity. CRS was graded by consensus criteria (Lee, Blood 2014) and neurotoxicity and other adverse events were graded by CTCAE v4.03. Response was evaluated according to 2008 IWCLL criteria.
Results
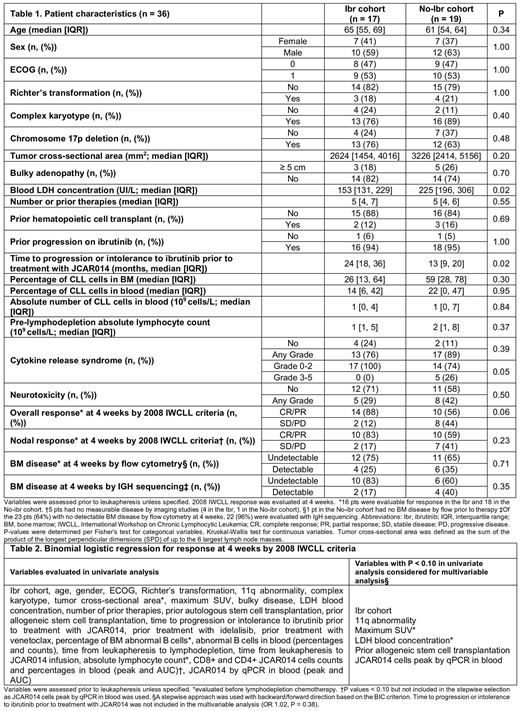
Seventeen and 19 pts were treated in the Ibr and No-ibr cohorts, respectively. Pt characteristics were comparable (Table 1). Progression on ibrutinib was noted in 16 (94%) and 18 pts (95%) in the Ibr and No-ibr cohorts, respectively, and prior ibrutinib intolerance was reported in 1 pt in each cohort. The time to intolerance or failure of ibrutinib prior to treatment with JCAR014 was longer, and the pre-leukapheresis LDH was lower in the Ibr compared to the No-ibr cohort. The median follow-up in responders was 98 and 764 days in the Ibr and No-ibr cohorts, respectively.
Administration of ibrutinib with Cy/Flu and JCAR014 was well tolerated in most pts; ibrutinib was reduced or discontinued in 6 pts (35%) at a median of 21 days after JCAR014 infusion. In the Ibr cohort, 1 pt with grade 2 CRS developed fatal presumed cardiac arrhythmia and 1 pt developed a subdural hematoma in the setting of trauma and thrombocytopenia. No differences in the incidences of grade ≥3 cytopenias were observed. Concurrent ibrutinib administration did not appear to affect the frequency or severity of neurotoxicity. Although the proportions of pts with grade ≥1 CRS were similar between cohorts (76% vs 89%, P = 0.39), the severity of CRS (grade ≥3 CRS: Ibr, 0%; No-Ibr, 26%; P = 0.05) and serum peak IL-8 (P = 0.04), IL-15 (P = 0.003) and MCP-1 (P = 0.004) concentrations were lower in the Ibr cohort. However, we found comparable CD8+ (P = 0.29) and higher CD4+ (P = 0.06) CAR-T cell counts in blood in the Ibr cohort.
Sixteen pts (94%) and 18 pts (95%) in the Ibr and No-ibr cohorts, respectively, have completed response assessment. We observed a higher proportion of responders (complete and partial remission) by IWCLL criteria in the Ibr compared to the No-ibr cohort (88% vs 56%, respectively, P = 0.06). Ten of 12 pts (83%) with lymph node disease before treatment with Cy/Flu and JCAR014 in the Ibr cohort achieved CR or PR by IWCLL imaging criteria, compared to 10/17 pts (59%) in the No-ibr cohort (P = 0.23). The proportion of pts with pretreatment bone marrow (BM) disease who had no disease by flow cytometry after CAR-T cell immunotherapy was similar in the Ibr compared to the No-ibr cohort (75% vs 65%, P = 0.71). However, among pts with no disease by BM flow cytometry after CAR-T cell immunotherapy, a higher proportion of pts in the Ibr cohort had no malignant IGH sequences at 4 weeks (83% vs 60%, respectively, P = 0.35). We performed univariate logistic regression analysis for response by IWCLL criteria and variables with P < 0.10 were considered for stepwise multivariable analysis (Table 2). In the multivariable analysis, the Ibr cohort and a lower pre-treatment SUVmax on PET imaging were each associated with a higher probability of response by IWCLL criteria (Ibr cohort, OR = 14.02, 95%CI [0.52-379.61], P = 0.05; SUVmax, OR = 1.31 per SUV unit decrease, 95%CI [1.05-1.67], P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Administration of ibrutinib from 2 weeks before leukapheresis until 3 months after JCAR014 was well tolerated in most pts. This approach might decrease the incidence of severe CRS and improve responses in pts with R/R CLL.
Hirayama:DAVA Oncology: Honoraria. Hay:DAVA Oncology: Honoraria. Li:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Lymp:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Till:Mustang Bio: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Kiem:Magenta: Consultancy; Homology Medicine: Consultancy; Rocket Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Shadman:TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Qilu Puget Sound Biotherapeutics: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy; Beigene: Research Funding; Mustang: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy. Cassaday:Merck: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Other: Spouse Employment, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Acharya:Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Teva: Honoraria. Riddell:Juno Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; NOHLA: Consultancy; Cell Medica: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Maloney:GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Honoraria; Janssen Scientific Affairs: Honoraria. Turtle:Nektar Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics / Celgene: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Aptevo: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Caribou Biosciences: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Eureka Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal